ICE LAB - Whole Body Cryotherapy
Principles of WBC
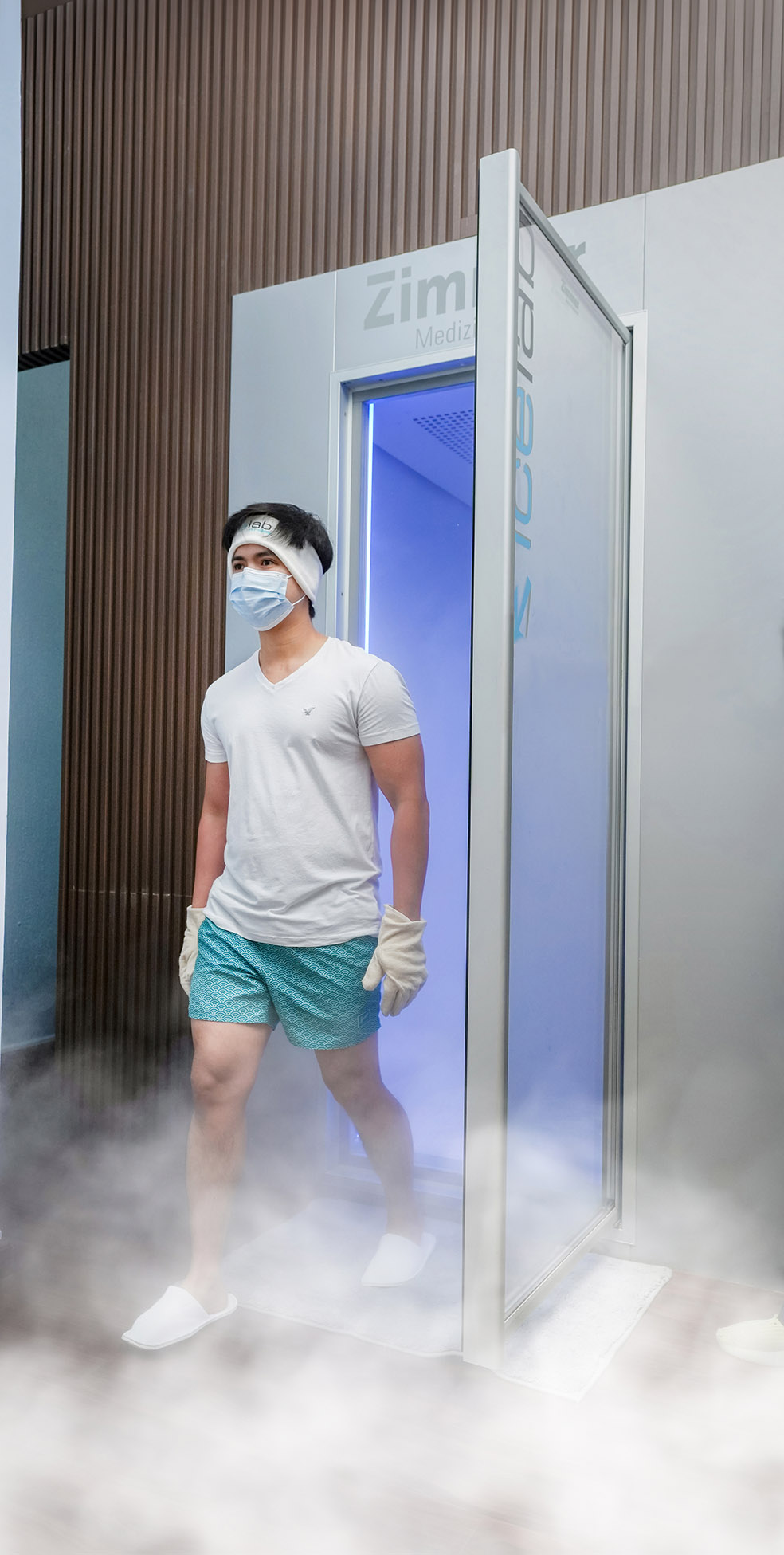
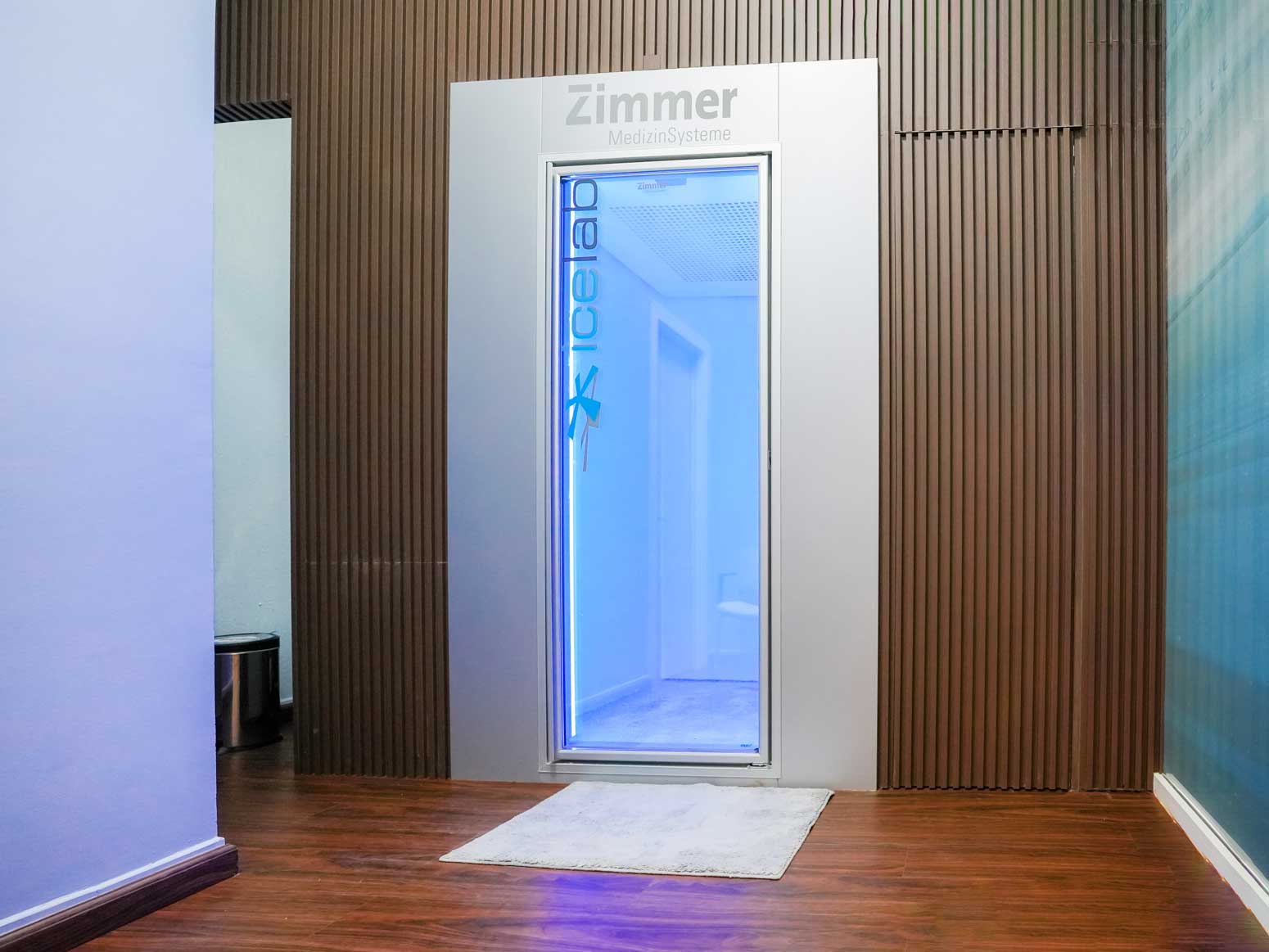
Whole-body cryotherapy is the therapeutic application of extreme cold for a short time (up to 3 min) which stimulates the body's natural healing mechanism by stimulating the circulatory system, the nervous system and the energy meridians.
This extreme cold application helps with inflammation and reduces pain and other symptoms.
Brief exposure (up to 3 minutes) to an extreme (dry) cold over the entire body
- Lowers the surface temperature of the skin by an average of 14°C
- Lowers the surface temperature of the skin by an average of 14°C
Cold shock (stimulus-response principle)
- Positive influence on musculoskeletal system, nervous system, cardiovascular system and endocrine system.

Areas of Application
Pain management, Inflammation control
Recovery and Performance enhancement
Anti-ageing, Skin Rejuvenation, Relaxation
Weight loss, Metabolism improvement
Sleep disorders, Jet lag, Relaxation
Pain & Inflammation Management
The anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of Whole- Body Cryotherapy greatly decrease the pain and stiffness of rheumatoid and osteoarthritis.
The body's response to cryotherapy is an increase in endorphins. The principle function of endorphins is to inhibit the transmission of pain signals; these endorphins decrease pain sensitivity providing an effective, completely natural and noninvasive pain therapy.

Areas of Application
Cryotherapy is used in Sports and Fitness for healing, recovery and performance improvement. Athletes and sports enthusiasts enjoy Whole Body Cryotherapy treatments before or after a workout to boost performance, decrease fatigue and muscle pain, and speed up the recovery.
Whole Body Cryotherapy is effective in reducing exercise-induced muscle damage (EIMD) and inflammation by vasoconstriction at muscular level and an increase in anti-inflammatory cytokines.
Whole Body Cryotherapy session prior to sports is believed to have a positive impact on performance of the athletes.
Weight Loss
A single Whole Body Cryotherapy treatment can burn 500-800 calories throughout the day. When exposed to sudden cold temperatures, the body burns fat for instant energy to produce heat and keep body temperatures. This increases the metabolic rate and helps burn more calories faster.
This effect lasts from 4-6 hours after the application of extreme cold. After several sessions, the metabolism rate remain higher even between sessions.


Anti-Ageing and Skin Rejuvenation
Cryo treatments improve skin by boosting oxygen and nutrient supply to the skin. The outer layers of skin are briefly "frozen" leading to collagen production in deeper layers of the skin. This leads to greater skin elasticity giving the user tighter and firmer skin as well as a more youthful appearance.
The anti-inflammatory properties of cryotherapy are used to treat conditions such as dermatitis and psoriasis, also helping with various levels of acne.
Sleep Disorders
The extreme temperatures of Whole body Cryotherapy commence a 'fight or flight' response, releasing inhibitory neuropeptides called endorphins, a natural 'pain killer' implementing a sense of euphoria. It has a positive effect on insomnia, moods and sleep patterns.
This effect lasts from 4-6 hours after the application of extreme cold. After several sessions, the metabolism rate remain higher even between sessions.

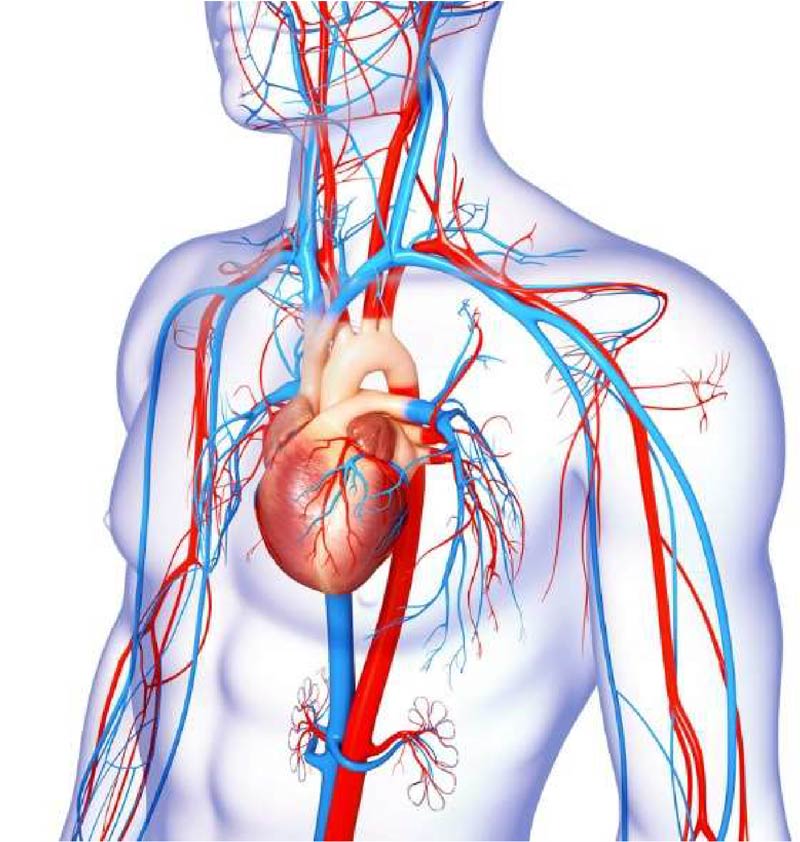
Improvement of Circulation
The freezing temperatures in Cryotherapy makes the body reacts to cold, increasing blood circulation which makes it easier to deliver oxygen, nutrients, and enzymes throughout the body.
Indications
- Fibromyalgia
- Muscle Pain and Inflammation
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Chronic Pain Syndrome
- Inflammation of Tendons, Bursa, Joint Capsules
- Degenerative Disease of Joints and Spine
- Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness
- Depression and Mood Disorders
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
- Phantom Pain
Contra-Indications
Untreated high blood pressure (160/100 mmHg)
Myocardial infarction
(< 6 months)
lschemic heart disease
Cardiac arrhythmia
Peripheral arterial disease
Venous thrombosis
Decompensated diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems
Acute febrile Respiratory disease
Acute kidney and urinary tract diseases
Haemophilia
Cardiac pacemaker
Severe anaemia
Pregnancy from 4th month onwards
Under the influence of alcohol and drugs
History of Epileptic Seizures
Raynaud syndrome
Polyneuropathy
Vasculitis
Claustrophobia
Symptoms of Cold allergy
Hypothyroidism
